What is a Use Case Diagram?
A use case diagram is a type of drawing that shows how different people (called “actors”) interact with a system (like a software program or website). It’s a way to show what the system does and who uses it.
Key Notions (Symbols) in a Use Case Diagram:
Actors:
- Stick Figure: Represents a person or thing that interacts with the system. For example, a student, teacher, or librarian.
Use Cases:
- Oval: Represents a task or activity that the system performs. For example, “Borrow a Book”, “Return a Book”, or “Search for a Book”.
System Boundary:
- Rectangle: Represents the system we’re discussing. Everything inside the rectangle is part of the system. For example, “Library Management System”.
Associations:
- Lines: Show which actors are involved in which use cases. A line connects an actor to a use case they participate in.
Relationships:
Generalization:
- Arrow with a Triangle: Shows that one actor or use case is a special type of another. For example, “Teacher” and “Student” are special types of “Library User”.
Include:
- Dashed Arrow with «include»: Shows that a use case always uses another use case. For example, “Borrow a Book” always includes “Check Book Availability”.
Extend:
- Dashed Arrow with «extend»: Shows that a use case sometimes uses another use case. For example, “Return a Book” might extend to “Pay Late Fees” if the book is returned late.
Example: Library Management System
Let’s create a simple use case diagram for a library management system:
Actors:
- Student: Uses the library to borrow and return books.
- Teacher: Also borrows and returns books, and may add new books to the library.
- Librarian: Manages the library, adds books, checks inventory.
Use Cases:
- Borrow a Book
- Return a Book
- Add a Book
- Check Inventory
- Pay Late Fees
Diagram Explanation:
- Student and Teacher are connected to Borrow a Book and Return a Book because they both use these functions.
- Librarian is connected to Add a Book and Check Inventory because they manage these tasks.
- Return a Book is connected to Pay Late Fees with an «extend» relationship because paying late fees is an additional step that only happens sometimes.
- Borrow a Book includes Check Book Availability because every time someone borrows a book, the system must check if the book is available.
Here’s a simplified version of what this diagram looks like:
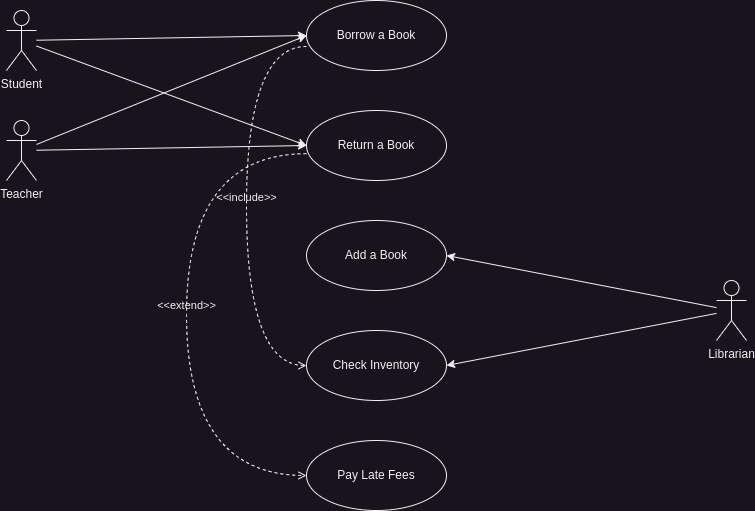
In this diagram:
- Students and Teachers can Borrow a Book and Return a Book.
- Librarians can Add a Book and Check Inventory.
- Returning a Book can sometimes lead to Paying Late Fees.
This is a basic overview, and use case diagrams can get more complex with more actors and use cases. But the main idea is to show who does what with the system and how different tasks are related.